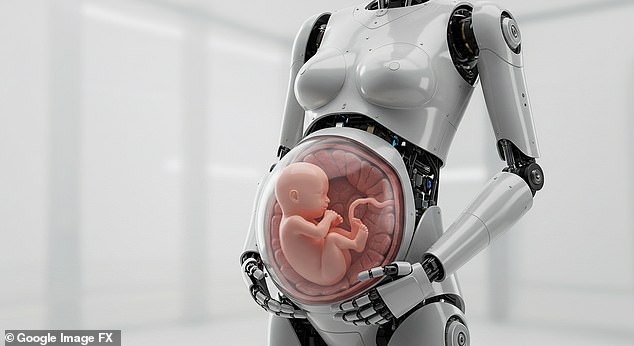
It’s a concept that currently only exists in sci–fi movies.
But scientists in China are developing the world’s first ‘pregnancy robot’ capable of carrying a baby to term and giving birth.
The humanoid will be equipped with an artificial womb that receives nutrients through a hose, experts said.
A prototype is expected to be released next year, with a selling price of around 100,000 yuan (£10,000).
Dr Zhang Qifeng, who founded the company Kaiwa Technology, is developing the machine.
The device he envisions is not simply an incubator but a humanoid that can replicate the entire process from conception to delivery, Asian media outlets report.
He said the artificial womb technology is already in a ‘mature stage’ and now needs to be implanted in the robot’s abdomen, ‘so that a real person and the robot can interact to achieve pregnancy’.
With regards to ethical and legal issues, he said: ‘We have held discussion forums with authorities in Guangdong Province and submitted related proposals while discussing policy and legislation.’

The humanoid will be equipped with an artificial womb that receives nutrients through a hose, experts said (AI–generated image)

The development is reminiscent of the 2023 film The Pod Generation, where a tech giant offers couples the option of using detachable artificial wombs or ‘pods’ to share pregnancy
Experts have not yet provided any specifics on how the egg and sperm are fertilised and implanted in the artificial womb.
Dr Zhang’s revelations were made during an interview shared on Duoyin, the Chinese version of TikTok.
News of the development sparked intense discussion across Chinese social media, with critics condemning the technology as ethically problematic and unnatural.
Many argued that depriving a foetus of maternal connection was cruel, while questions were raised about how eggs would be sourced for the process.
However, many showed support for the innovation, viewing it as a means to spare women from pregnancy–related suffering.
One wrote: ‘Many families pay significant expenses for artificial insemination only to fail, so the development of the pregnancy robot contributes to society.’
Previously, scientists have successfully kept premature lambs alive for weeks using an artificial womb that looks like a plastic bag.
The ‘biobag’ provided everything the foetus needed to continue growing and maturing, including a nutrient–rich blood supply and a protective sac of amniotic fluid.

In trials, researchers have shown that premature lambs kept in artificial wombs not only survived but put on weight and grew hair (pictured)
After 28 days of being in the bag, the lambs – which otherwise would likely have died – had put on weight and grown wool.
While the biobag acts like an incubator, allowing premature individuals to grow in an environment similar to the womb, scientists hope the pregnancy robot will be able to support the foetus from conception to delivery.
Since the 1970s, feminist activists such as Andrea Dworkin have been strongly opposed to the use of artificial wombs on the grounds that it could lead to the ‘end of women’.
In 2012, Ms Dworkin wrote: ‘Women already have the power to eliminate men and in their collective wisdom have decided to keep them.
‘The real question now is, will men, once the artificial womb is perfected, want to keep women around?’
In 2022 a group of researchers from The Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia – who have been developing artificial wombs – published an article on the ethical considerations of technology.
The researchers wrote: ‘A concern is that it could lead to the devaluation or even pathologizing of pregnancy, and may diminish women’s experience of deriving meaning, empowerment, and self–fulfillment from this unique aspect of female biology.’
Earlier this year, however, a survey showed that 42 per cent of people aged 18–24 said they would support ‘growing a foetus entirely out of woman’s body’.

Artificial wombs, like this concept showcased by Eindhoven University in 2019, allow a child to be raised without a biological mother. In a survey conducted by the think–tank Theos, 42 per cent of people aged 18–24 said they would support ‘growing a foetus entirely outside of a woman’s body’
The development is reminiscent of the 2023 film The Pod Generation, where a tech giant offers couples the option of using detachable artificial wombs or ‘pods’ to share pregnancy.
If it comes to fruition, the humanoid pregnancy could be seen as a tool to help tackle rising rates of infertility in China.
Reports suggest the rates of infertility in China rose from 11.9 per cent in 2007 to 18 per cent in 2020.
In response, local governments in China are including artificial insemination and in vitro fertilization treatments in medical insurance coverage to support childbirth for infertile couples.
This article was originally published by a www.dailymail.co.uk . Read the Original article here. .